Maximum Segment Size (MSS) in Networking: What is it?
In the world of networking, Maximum Segment Size (MSS) plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient data transmission. MSS is a parameter used in the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) that specifies the largest segment of data a device can receive in a single TCP packet. Understanding MSS can help optimize network performance, reduce latency, and prevent fragmentation.
What is Maximum Segment Size (MSS)?
Maximum Segment Size (MSS) defines the maximum amount of data, in bytes, that can be transmitted in a single TCP segment, excluding the TCP and IP headers. The MSS value is typically determined during the TCP three-way handshake, where both communicating devices negotiate an appropriate MSS based on their network constraints.
How do MSSs work?
When a TCP connection is established, each device advertises its MSS value in the SYN packet. The effective MSS used in the communication is the smaller of the two advertised values. MSS is important because it helps prevent packet fragmentation, which can lead to inefficiencies in data transmission.
For example, if a device sets an MSS of 1460 bytes, this means it can receive up to 1460 bytes of data in a single TCP segment. Since an Ethernet frame has a standard Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of 1500 bytes and includes 40 bytes for the TCP (20 bytes) and IP headers (20 bytes), the MSS is typically set to MTU – 40 bytes.
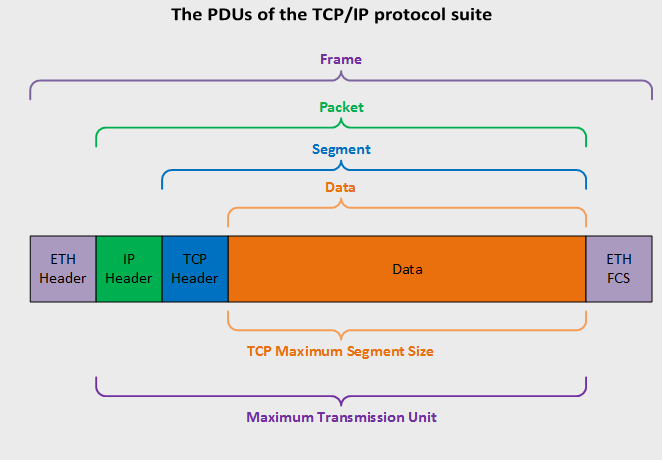
Maximum Segment Size (MSS) vs Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)
It’s important to distinguish between MSS and MTU:
- MTU refers to the total maximum packet size, including headers.
- MSS refers to the maximum data payload that can be carried within the TCP segment.
- MSS = MTU – (TCP + IP headers)
Understanding the relationship between MSS and MTU helps in avoiding packet fragmentation and ensuring optimal network performance.
Importance of MSS in Networking
- Reduces Fragmentation: Proper MSS configuration prevents data from being split across multiple packets, reducing reassembly overhead.
- Optimizes Bandwidth: By setting an appropriate MSS, network congestion and retransmissions are minimized.
- Enhances Performance: A well-configured MSS value ensures faster data transfer by reducing unnecessary overhead.
- Prevents Transmission Errors: Incorrect MSS settings can lead to excessive fragmentation, increasing packet loss and retransmissions.
How to Configure Maximum Segment Size
MSS can be manually set on network devices such as routers, firewalls, and computers. Common ways to configure MSS include:
- Router Configuration: Many routers allow administrators to set an MSS clamp to ensure TCP packets comply with network MTU limits.
- Operating System Settings: Some operating systems allow users to tweak TCP settings to optimize MSS values.
- Firewalls and Proxies: Security devices often enforce MSS values to avoid excessive fragmentation and improve security.
Common Maximum Segment Size Values
| Network Type | Typical MTU | MSS Value |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet | 1500 bytes | 1460 bytes |
| PPPoE | 1492 bytes | 1452 bytes |
| IPv6 | 1280 bytes | 1240 bytes |
| DSL | 1452 bytes | 1412 bytes |
Conclusion
Understanding and configuring Maximum Segment Size (MSS) is essential for optimizing network performance. By ensuring MSS values align with network MTU settings, administrators can minimize fragmentation, enhance efficiency, and improve data transmission speeds. Proper MSS tuning is a critical aspect of network management and plays a vital role in ensuring seamless connectivity.