Centralized Network: Everything you need to know
What is a Centralized Network?
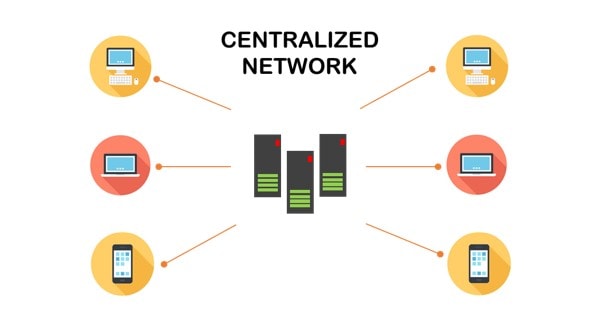
A centralized network is a system where a single central authority or server manages all the network’s data and resources. This centralized control ensures streamlined management, higher efficiency, and easier implementation of security measures. It is commonly used in organizations, cloud computing systems, and many internet-based services.
How does it work?
In a centralized network, all client devices, such as computers or smartphones, connect to a central server as the primary hub for data exchange and resource allocation. The server manages all requests, processes data, and ensures the smooth operation of the entire network. This setup enables the central authority to monitor and control all activities within the network.
Advantages of a Centralized Network
- Simplified Management: Centralized control makes managing resources, updates, and security policies easier.
- Cost-Effective: By consolidating resources into a single system, businesses can reduce costs related to hardware and maintenance.
- High Security: A centralized system allows for the implementation of uniform security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Efficient Data Processing: Centralized servers can process and manage large amounts of data more effectively than decentralized systems.
- Ease of Deployment: Setting up a centralized network is generally quicker and less complex than deploying a decentralized system.
Disadvantages of a Centralized Network
- Single Point of Failure: If the central server fails, the entire network may become inoperable.
- Scalability Issues: As the network grows, the central server might struggle to handle increased traffic and resource demands.
- Potential Latency: In some cases, data requests might experience delays due to high server loads.
- Vulnerability to Attacks: It can be targeted by cyber attacks, such as Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, which may disrupt operations.
Examples of Centralized Networks
- Banking Systems: Banks rely on centralized networks to manage customer data, transactions, and operations efficiently.
- Social Media Platforms: Services like Facebook and Instagram use centralized servers to store user data and manage interactions.
- Corporate Intranets: Many businesses utilize centralized networks to share resources and facilitate communication within the organization.
- Cloud Services: Platforms like Google Drive and Dropbox depend on centralized servers to provide seamless data storage and sharing.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Networks
While centralized networks offer simplicity and control, decentralized networks distribute data and decision-making across multiple nodes. Decentralized systems, such as blockchain technology, are more resilient to failures and attacks but can be more complex to manage and scale.
Conclusion
Centralized networks remain a cornerstone of modern technology, powering many of the systems and services we rely on daily. They provide efficiency, security, and ease of management but come with challenges such as vulnerability to failure and scalability issues. Understanding the strengths and limitations of centralized networks is crucial for businesses and individuals when deciding on the right network architecture for their needs.