What is a Network Access Server (NAS)?
What is a Network Access Server (NAS)?
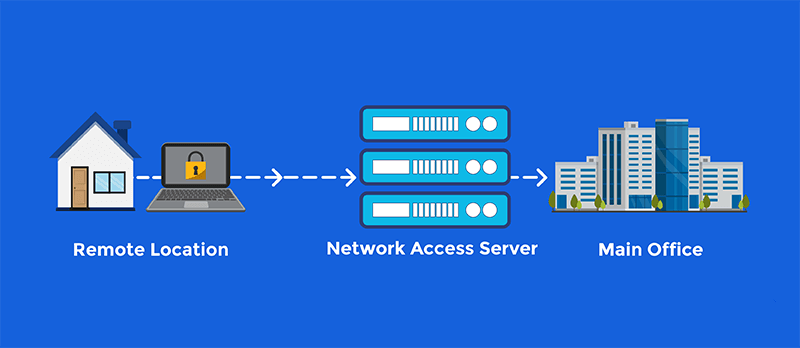
A Network Access Server (NAS) is a critical component in modern networking that serves as a gateway between users and a network. It acts as an intermediary device, enabling users to gain access to network resources through various authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) protocols. Whether for internet service providers (ISPs), corporate networks, or remote access systems, the NAS plays a vital role in ensuring secure and efficient connectivity.

Key Functions of a Network Access Server
- Authentication: The NAS verifies the identity of users attempting to access the network. This process ensures that only authorized individuals or devices can connect. Common authentication methods include: Password-based login, Multi-factor authentication (MFA), and Biometric verification.
- Authorization: After successful authentication, the NAS determines the level of access granted to the user. It ensures users can only access resources they are authorized to use based on pre-defined policies.
- Accounting: The network access server keeps track of user activity during a session. This includes data such as session duration, data usage, and login/logout times. These records are crucial for billing, monitoring, and compliance purposes.
Common Use Cases for NAS
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs) – NAS devices are widely used by ISPs to manage user connections, enforce subscription policies, and track data usage for billing.
- Corporate Networks – In enterprise environments, NAS enables secure remote access for employees, ensuring only authorized users can connect to internal systems.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – NAS devices are integral to VPNs, providing secure and authenticated access to remote users while encrypting their data traffic.
Types of Network Access Servers
- Dial-Up NAS: Traditionally used for dial-up internet connections, these devices authenticate and manage users connecting via telephone lines.
- Broadband NAS: Commonly used for DSL or cable internet connections, these devices handle high-speed data traffic and support multiple users simultaneously.
- Wireless NAS: Found in Wi-Fi networks, these devices manage access for users connecting wirelessly.
- Cloud-Based NAS: Emerging as a modern solution, cloud-based NAS offers scalability and flexibility for businesses, allowing seamless integration with cloud services.
Benefits of Using a Network Access Server
- Enhanced Security – By authenticating and authorizing users, NAS helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive network resources.
- Efficient Resource Management – NAS ensures that network resources are allocated effectively, avoiding congestion and optimizing performance.
- Scalability – Modern NAS solutions can scale to accommodate growing numbers of users and devices, making them ideal for expanding networks.
- Comprehensive Monitoring – With accounting capabilities, NAS provides detailed insights into user activity, aiding in compliance and operational planning.
How to Choose the Right NAS
When selecting a Network Access Server for your network, consider the following factors:
- User Capacity: Ensure the NAS can handle your current and future user base.
- Supported Protocols: Look for compatibility with popular AAA protocols such as RADIUS and TACACS+.
- Security Features: Opt for a NAS with robust encryption and authentication methods.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure the NAS integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructure and third-party tools.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your network requirements.
Conclusion
A Network Access Server is an indispensable tool for managing and securing network access. By performing essential functions like authentication, authorization, and accounting, it ensures that networks operate efficiently and securely. Whether for an ISP, a corporate environment, or a remote access solution, investing in the right NAS can significantly enhance network performance and user experience. As networking technology continues to evolve, the role of NAS will remain central to enabling seamless and secure connectivity.