What is a Network Mapper?
In today’s digitally connected world, understanding your network is crucial for both security and performance. One essential tool in a network administrator’s toolkit is the network mapper. Whether you’re managing a small office network or a large enterprise infrastructure, a network mapper can provide deep visibility into your connected devices, open ports, and potential vulnerabilities.
What is a Network Mapper?
A network mapper is a tool used to discover devices on a network, identify their IP addresses, and gather detailed information about their configurations and services. It maps out the network structure and helps visualize how different components interact, making monitoring and securing the network easier.
Key Functions of a Network Mapper:
- Network Discovery: Detects all devices connected to a network.
- Port Scanning: Identifies open ports and services running on devices.
- OS Detection: Attempts to determine the operating systems of discovered devices.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Some advanced mappers detect known security flaws.
- Topology Mapping: Creates a visual representation of the network layout.
Why Does Use It?
Using a network mapper provides multiple benefits:
- Improved Network Security: By revealing unauthorized devices or open ports, you can take preventive action before threats emerge.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: Quickly locate problems in the network, such as bottlenecks or misconfigured devices.
- Compliance Monitoring: Helps organizations meet cyber security standards by maintaining an accurate inventory of network assets.
- Performance Optimization: Understand network traffic flow and optimize configurations for better speed and reliability.
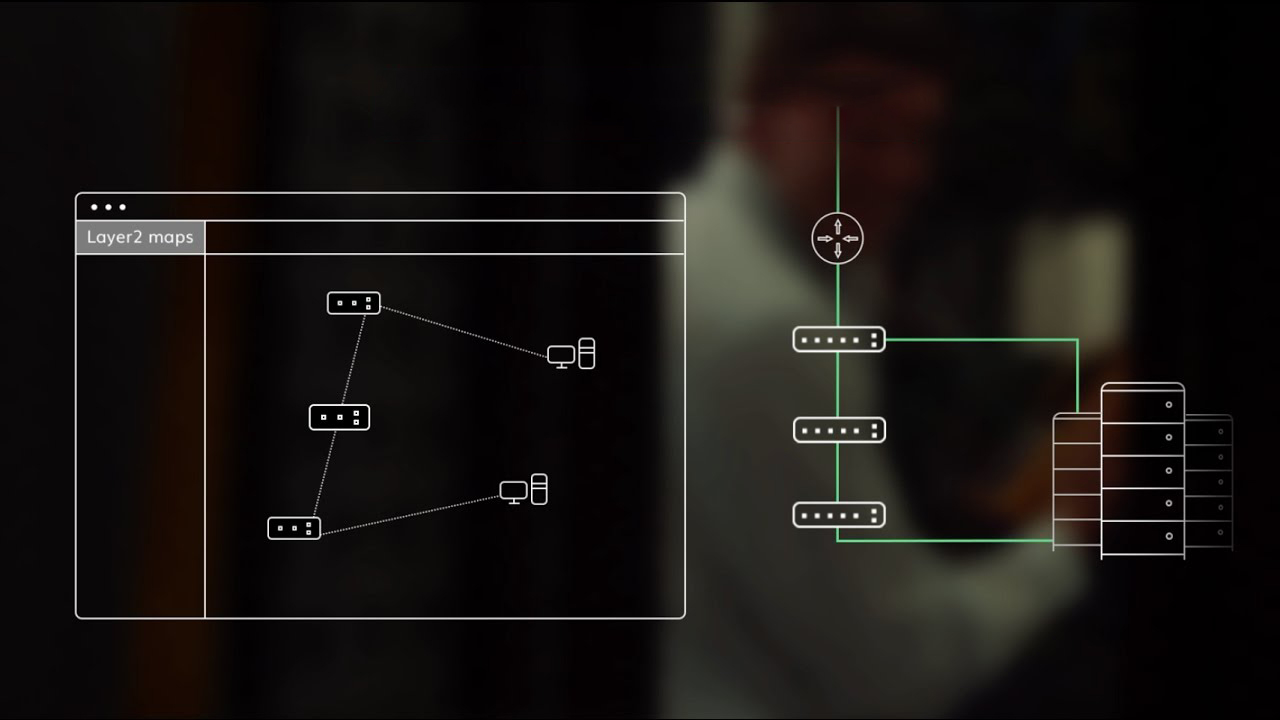
Popular Network Mapper Tools
Here are some of the most widely used network mapper tools:
1. Nmap
One of the most powerful and popular open-source network mapping tools, Nmap can perform detailed scans, detect operating systems, and even run scripts for advanced discovery.
- Pros: Highly customizable, scriptable, and free.
- Use Case: Ideal for security audits and penetration testing.
2. Zenmap
Zenmap is the official GUI for Nmap, making it more accessible for users who prefer a visual interface.
- Pros: User-friendly, provides network topology maps.
- Use Case: Great for beginners learning how to scan networks.
3. SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper
A commercial tool that automatically discovers and maps your network with real-time updates.
- Pros: Professional interface, real-time mapping, customizable reports.
- Use Case: Suitable for enterprise IT environments.
4. Advanced IP Scanner
A free and easy-to-use tool for Windows that provides fast network scans and remote control of devices.
- Pros: Lightweight, supports remote desktop and shutdown.
- Use Case: Best for small to medium-sized networks.
How to Use It Effectively
Here are a few best practices for using network mappers:
- Define Your Goals: Determine whether you’re scanning for inventory, vulnerabilities, or troubleshooting.
- Start with a Ping Sweep: Identify live devices before diving into deeper scans.
- Scan During Off-Hours: Avoid impacting network performance during peak usage.
- Document Findings: Maintain updated network diagrams and reports.
- Automate Regular Scans: Schedule scans to keep tabs on network changes.
Final Thoughts
A network mapper is a critical tool for anyone managing or securing a network. Whether you’re a system administrator, cybersecurity professional, or tech enthusiast, understanding your network layout can lead to stronger security, smoother operations, and more efficient troubleshooting. By using tools like Nmap, Zenmap, or commercial alternatives, you can maintain better control over your network infrastructure and quickly respond to potential threats.