What is a Neural Network?
Neural networks are a cornerstone of artificial intelligence (AI), revolutionizing industries by enabling machines to learn and make decisions. From powering voice assistants to diagnosing diseases, neural networks play a pivotal role in today’s technological advancements. This article dives into the fundamentals of neural networks, their working mechanism, types, and applications, offering an SEO-friendly and informative guide for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
What is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a computational model inspired by the human brain’s structure and functionality. It consists of interconnected nodes, or “neurons,” that process and analyze data. Neural networks are designed to recognize patterns, classify information, and make predictions, mimicking cognitive processes.
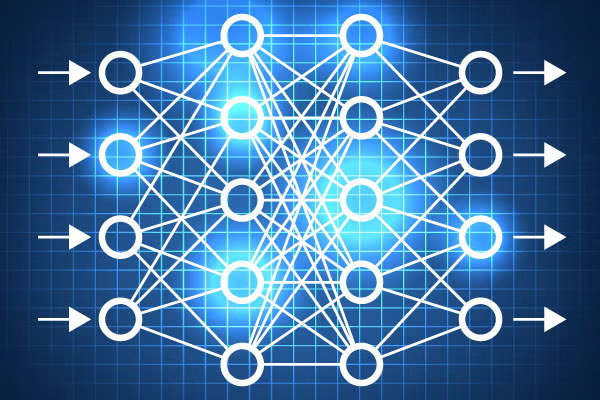
How does it work?
Neural networks function through layers of neurons:
- Input Layer: Receives raw data, such as images or text.
- Hidden Layer: Process the data using weighted connections and activation functions. These layers extract features and patterns.
- Output Layer: Provides the final result, such as a classification or prediction.
Each connection between neurons has a weight that adjusts during training to optimize the network’s performance. The training process involves feeding data into the network, calculating errors, and updating weights using algorithms like backpropagation.
Types of Neural Network
- Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs): The simplest type, where data flows in one direction. Ideal for tasks like image recognition and regression analysis.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Specialized for image and video processing, leveraging convolutional layers to detect spatial features.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Designed for sequential data like time series or text, with feedback loops for memory.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Comprising two networks, a generator, and a discriminator, GANs are used for creating realistic images, videos, and more.
- Transformer Networks: Widely used in natural language processing (NLP) tasks, they enable advancements in machine translation, text summarization, and chatbots.
Applications of Neural Network
Neural networks are integral to various industries:
- Healthcare: Disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
- Finance: Fraud detection, stock market prediction, and risk assessment.
- Retail: Recommendation systems, inventory management, and customer behavior analysis.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles and traffic prediction.
- Entertainment: Content recommendation and video game AI.
Benefits of Neural Network
- Accuracy: High precision in pattern recognition and predictions.
- Adaptability: Ability to learn from new data and improve performance.
- Scalability: Applicable to diverse fields and scalable with increasing data.
Challenges of Neural Networks
- Data Dependency: Requires large datasets for effective training.
- Computational Cost: High resource consumption for training and inference.
- Interpretability: Complex models can be difficult to understand and explain.
Future of Neural Network
The future of neural networks is promising, with advancements in quantum computing, edge AI, and deep learning architectures. Innovations in these areas are expected to enhance efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and broaden applications.
Conclusion
Neural networks are transforming the digital landscape, offering powerful solutions to complex problems. By understanding their structure, operation, and potential, businesses and individuals can leverage this technology to drive innovation and growth. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, exploring neural networks can unlock endless opportunities in the world of AI.