What is Hybrid Topology?
In computer networks, different types of network topologies are utilized to interconnect devices. One of the most popular topologies widely utilized nowadays is the Hybrid topology (a.k.a. hybrid network), which combines two or more different topologies.
What is Hybrid Topology?
A hybrid topology is a type of network topology that uses two or more differing network topologies. These topologies can include a mix of bus topology, mesh topology, ring topology, star topology, and tree topology.
The choice to use a hybrid topology over a standard topology depends on the needs of a business, school, or the users. How many computers need to be connected, their location and the desired network performance are all factors in the decision.

Hybrid Topology in Computer Network
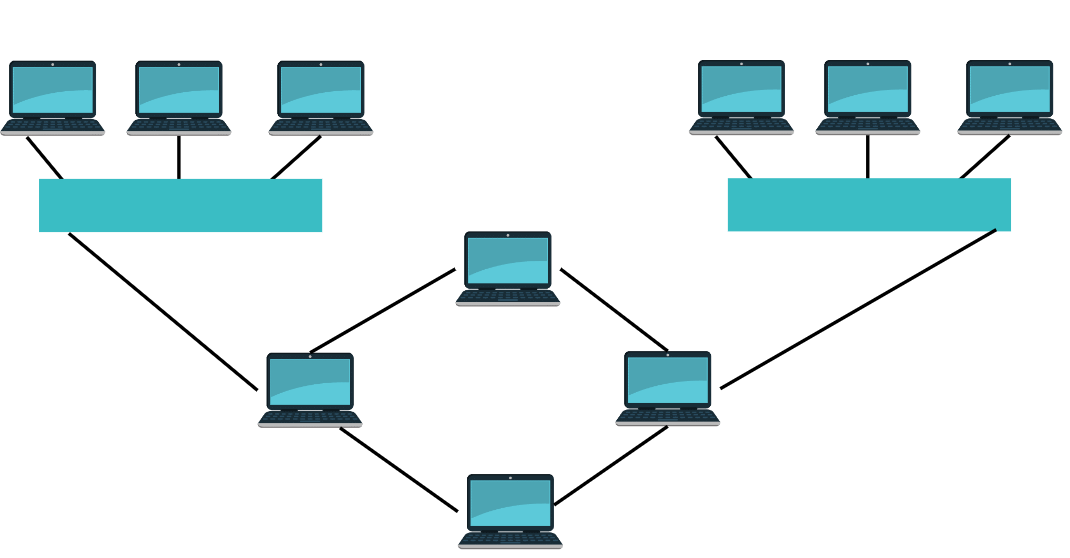
In a computer network, we use different kinds of network topologies like Bus, Star, Ring, and Mesh. However, the most frequently used network topology is Hybrid topology because it is the combination of two or more topologies. For instance, if you combine star and ring topology to make a large network through the hubs & switches then it is known as hybrid topology. The structure of the hybrid topology is shown below.
In the above network, two or more network topologies are interconnected and each topology has its own nodes. The resulting interconnection simply allows the nodes within a specified basic topology to communicate with other nodes in a similar basic topology and those in another basic topology in the hybrid network.
In this type of topology, we can select what will be the network backbone like a switch/ hub, and also divisions of the network that mainly vary because of its topological arrangement. The network divisions include the network topologies. The entire computer networking system mainly depends on the backbone of the network that is connected through network segments.
The hybrid network can be arranged at any place easily like a home or office because of the ease of use & flexibility. Because of the hybrid structure, each topology’s overall features are distributed equally in the series of networks which provides the easiest way to identify errors & also assist while doing troubleshooting.
Why do we use it?
Due to effective cost, different applications use hybrid topology. As compared to other fundamental mechanisms, the mechanism of hybrid topology is efficient; it can also be deployed in different environments. Thus, it provides users the benefit to create, run, and manage the organization. There are various sectors where the hybrid topology is widely used, such as many educational institutions, the banking sector, automated industries, the financial sector, research organizations, and multinational companies. For creating the structure of the new hybrid topology, there is a need to mix any two topologies like full mesh topology, extended star, partial star, point to point networks.
The examples and applications of hybrid topology are increasing rapidly. It has a super-power setup and flexible option and is declared as a smart option; hence, people choose to deploy it at home or office. A compact is provided for the small-scale industries by this topology, as well as for their subunits. Thus, it is good to use for multi-floor buildings and departments such as an office or home. This topology is placed to give its maximum efficiency on the basis of the requirements as it provides many benefits.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
Flexibility in Network Design
It stands out for its unparalleled flexibility, offering tailored network solutions that cater to the unique needs and constraints of different network segments within an organization. Unlike rigid conventional topologies, hybrid topology allows network designers to employ the most appropriate topology—be it star, ring, bus, or mesh—in different parts of the organization based on specific requirements such as bandwidth needs, priority of data traffic, and geographic layout. For instance, a company might implement a star topology in its customer service department to ensure centralized management, while opting for a mesh topology in its R&D department to prioritize data redundancy and fault tolerance.
Scalability
The scalable nature of hybrid topology makes it an ideal choice for growing organizations. As a business expands, new nodes or even entire sub-networks with different topologies can be seamlessly integrated into the existing hybrid network. This scalability ensures that the network can grow in tandem with the organization, without necessitating a complete overhaul of the infrastructure. For example, a retail chain can easily add new stores to its network, each with its local star topology network, while maintaining a mesh topology for the head office and regional warehouses to ensure robust interconnectivity and data consistency across the entire organization.
Reliability and Fault Tolerance
It enhances the overall network reliability and fault tolerance by integrating multiple topologies, each with its inherent strengths. The failure of a single node or segment in one part of the network, governed by a specific topology, does not spell disaster for the entire network. This compartmentalization of risk means that issues can be isolated and addressed with minimal impact on the broader network. For instance, in a hybrid network combining star and ring topologies, the failure of a central hub in the star segment might disrupt local communications but will not affect the operations in the ring segment, ensuring the continuity of critical operations.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
- Complexity: To manage the topology becomes challenging, as the different topologies are linked in the hybrid topology. It is a difficult job for designers and not easy to create this type of architecture. There is a need to be very efficient in the installation and configuration process.
- Expensive: Purchasing and maintaining the hybrid topology is much more expensive when compared with other topologies. The hubs are also required in this network topology that are used to connect two different networks, and they are also expensive. Furthermore, the hybrid topology may need advanced network devices, a lot of cables, and more as its architectures are usually larger in scale.
- One of the other disadvantages of hybrid topology; although it can detect faults easily, it needs a multi-station access unit to bypass faulty devices.
Conclusion
Hybrid topology offers a versatile and efficient solution for complex and varied network requirements. Its ability to combine the strengths of different topologies makes it an ideal choice for large organizations and environments with diverse networking needs. While it presents challenges in terms of complexity and cost, the benefits of flexibility, scalability, and enhanced reliability often justify the investment in a hybrid network infrastructure. As technology evolves and organizations grow, hybrid topology continues to be a key player in the development of effective and robust network architectures.