File Server: How does it work?
Digital data plays a crucial role in our daily lives, as sharing and storing these files becomes more relevant in the digital age. One way to accomplish this is by using a file server. What most people don’t know is that File Servers are very important. Well, in this article, we will dig into the file server options that you may consider using and ideal for your storage needs.
What is a File Server?
A file server is a specialized computer within a network that handles the storage, retrieval, and management of data files for multiple users. It operates by providing a centralized location where files can be stored, ensuring that users on the network can access and share these files as needed. This centralization of data not only facilitates collaboration among users but also simplifies data management tasks such as backups, security updates, and data integrity checks.
File servers are particularly important in organizational environments where the efficient distribution of resources and access controls are necessary to maintain operational workflows. Moreover, they support various protocols that enable seamless communication and data exchange between different devices and operating systems within the network. Through its role, the file server enhances productivity by enabling more effective data sharing and management while ensuring that data security and access policies are upheld.
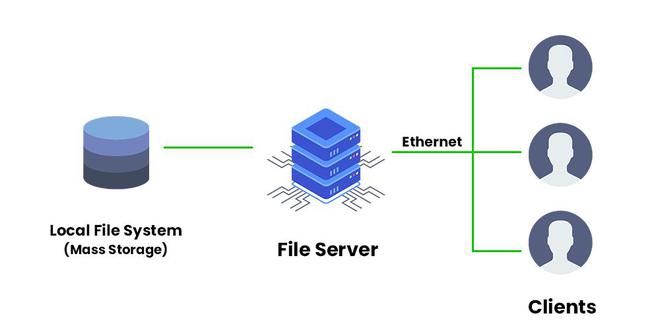
How does it work?
The right hardware is a necessity for a reliable file server. A hard drive with enough capacity to hold space or files, operating system, and client software is also important so that it has enough processing power and sufficient working memory to enable quick access to data and programs for multiple users.
Special network protocols control the communication between the clients and the file server. The SMB (Server Message Block) is commonly used in local networks running Windows, MacOS, and PCs with Unix-like systems. However, clients and file servers running Unix/Linux must have software installed that implements the SMB protocols to integrate the two protocols into one network.
The file transfer protocol or its encrypted version, secure FTO, is typically supported by the Internet which is used to access the file. However, you can also use other options such as HTTP-based WebDAV protocols and SCP (secure copy).
Advantages of File Server
There are a few benefits of file servers; such as:
- Less maintenance of your system
- Data is highly secured, and easy to get data backup.
- Easy to data recovery.
- Easy to handle all files centrally.
- It does not need a change of application programs while changing of physical file
- Use of versions in future releases to allow programs from a previous release to run against a changed database.
- Easy to transition from old database to new database.
- It helps to decrease the storage space pressure of the client system.
- It can be used on one file server at once without changing your entire system.
- A file server can be accessed remotely with using of WebDAV and SCP.
Disadvantages of File Server
There are limitations of file servers; like as:
- It may be costly if it is used in small companies, where two or three employees work.
- Require a well-qualified IT person to set up and administer.
- Increase network bandwidth while reading and writing files to and from the file server by all clients.
- If the file server gets halted then all files are lost until they can be recovered from backup.
Type of File Server
File Servers can be categorized as:
- Dedicated File Server: Dedicated File Server solely provides services to other computers. This can be in a particular local-area network or having a properly authorized access request associated with a computer system. It is dedicated to one purpose – being a File Server. A Dedicated File Server offers sufficient storage space for the website. Also, it is more secure.
- Non-Dedicated File Server: The function of a Non-Dedicated File Server is like any other workstation that permits it to utilize itself as a workstation. These File Servers can be used simultaneously as a workstation, and also for everyday tasks. A Non-Dedicated File Server offers less storage space for the website. It is less secure and can be compromised by a fraudster.
Most common File Server Protocols
File servers use different protocols to share files over the network. Each protocol offers different features, and these are the main ones used:
- SMB (Server Message Block): commonly used on Windows-based networks.
- NFS (Network File System): used for file sharing in UNIX and Linux-based systems.
- AFP (Apple Filing Protocol): used by Apple file servers to share files with Apple clients.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): used to transfer files over the Internet and between computer systems. Requires authentication for access, because the transferred data is not encrypted and vulnerable.
- SFTP (FTP over SSH): a secure version of FTP, which uses encryption to protect file transfers from unauthorized access or interception.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): easy to implement as users only need a web browser to access files and are less prone to firewall issues (unlike FTP).
- HTTPS (HTTP over SSL): a secure version of HTTP. Just like HTTP, no installation is needed on the client side.
- WebDAVs (Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning): runs over HTTP, allowing users at different locations to exchange and collaborate on the same files.

File Server Security
File servers store the most important data in an organization. Loss of this data will severely impact any business. File servers, therefore, need to be protected against failure, disaster, attack, and ransomware.
Backups are fundamental to operating file servers. A good backup will ensure that data is still available or recoverable in the case of hardware failure or attack.
The best practice is that several copies of important data be kept and that some of these copies should be at a different physical location and be offline or not connected to the network. This way, even if a natural disaster destroys a data center or if ransomware encrypts the file server, the files can be recovered. It is important to test file backups regularly.
File servers are a high-value target for attackers and so should be isolated from the internet. File permissions should be regularly audited. Regular updates can keep them from being exploited. Alerts or auditing should notify of strange activity to stop file exfiltration or encryption programs.
Conclusion
Have you ever used a File Server before to share or access files? This article has highlighted the significance and functionality of File Servers in a well-structured way. Using a File Server in a particular organization makes file transferring and sharing flexible and simple. Thus, it’s a great way to enhance work efficiency among multiple users within a safe ecosystem.