What is a Proxy Port?
In today’s digital landscape, proxies play a crucial role in enhancing security, anonymity, and access to restricted content. A key component of proxy servers is the proxy port, which dictates how data flows between clients and servers. In this guide, we will explore what a proxy port is, how it works, and why it is essential for online activities.
What is a Proxy Port?
A proxy port is a specific network port used by a proxy server to facilitate communication between a user’s device and the internet. When a user connects to a proxy server, their data is routed through a designated port, which ensures proper data transmission and reception.
Each proxy type operates on different ports, enabling various functionalities and security measures. Understanding these ports helps users optimize their browsing experience while maintaining privacy and security.
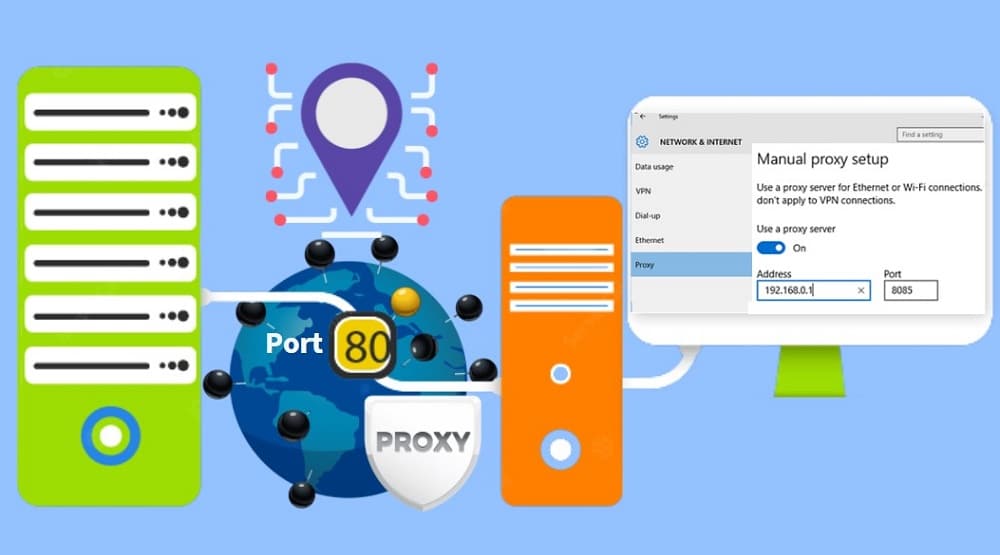
Common Proxy Ports and Their Uses
Different types of proxies utilize specific port numbers to function efficiently. Here are some of the most commonly used proxy ports:
- HTTP Proxy (Port 80, 8080, 3128): Primarily used for web traffic, HTTP proxies help users browse the internet anonymously or access restricted content.
- HTTPS Proxy (Port 443): Ensures secure communication by encrypting data, making it ideal for secure transactions and confidential browsing.
- SOCKS Proxy (Port 1080): A versatile proxy type that supports multiple protocols, including FTP, SMTP, and P2P connections.
- FTP Proxy (Port 21): Facilitates file transfers between users and servers, commonly used for remote file access.
How It Enhance Security and Privacy
Using a proxy port offers numerous benefits in terms of security and privacy. Some key advantages include:
- Anonymity: Proxy servers mask users’ IP addresses, making it difficult for websites to track their online activity.
- Geo-Restriction Bypass: Users can access content restricted to specific regions by routing their connection through proxy ports in different locations.
- Enhanced Security: Many proxies filter malicious traffic and encrypt data, reducing the risk of cyber threats.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Some proxy servers cache frequently accessed content, improving load times and reducing bandwidth consumption.
Choosing the Right Proxy Port for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate proxy port depends on your specific needs:
- For general web browsing, an HTTP or HTTPS proxy (Port 80 or 443) is ideal.
- If you need enhanced security, opt for a SOCKS proxy (Port 1080) with encryption capabilities.
- For file transfers, an FTP proxy (Port 21) ensures smooth data exchange.
Conclusion
Proxy ports are an essential aspect of proxy servers, ensuring seamless communication, security, and privacy. Understanding how they work and choosing the right proxy port for your needs can significantly improve your online experience. Whether for bypassing geo-restrictions, maintaining anonymity, or securing sensitive transactions, using the correct proxy port can make all the difference.
For businesses and individuals alike, leveraging proxy technology effectively can lead to safer, faster, and more reliable internet access. Stay informed and choose wisely to optimize your digital interactions!