Wireless Local Loop (WLL): A Comprehensive Guide
In the rapidly evolving world of telecommunications, Wireless Local Loop (WLL) has emerged as a game-changer. WLL technology is redefining how we connect to the internet and communicate, especially in areas where traditional wired infrastructure is challenging to implement. This article delves into the intricacies of WLL, its benefits, applications, and future potential.
What is the Wireless Local Loop (WLL)?
Wireless Local Loop (WLL) refers to a telecommunication system that connects subscribers to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or other communication networks using wireless technologies instead of traditional copper or fiber-optic cables. It is an efficient and cost-effective alternative to conventional wired solutions, particularly in remote or underdeveloped regions.

How Does WLL Work?
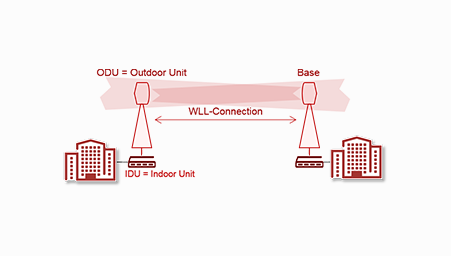
WLL operates by utilizing radio frequencies to establish communication between a subscriber’s premises and the base station. The key components of a WLL system include:
- Base Station: Acts as the central hub, transmitting and receiving signals to and from subscribers.
- Subscriber Units: Devices installed at the user’s location to facilitate communication with the base station.
- Core Network: Connects the base station to the broader telecommunications network, ensuring seamless integration.
By bypassing the need for physical cables, WLL significantly reduces infrastructure costs and deployment time.
Advantages of Wireless Local Loop
WLL offers several benefits that make it an attractive choice for telecommunication providers and users alike:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Eliminates the need for expensive cable installations, reducing overall infrastructure expenses.
- Rapid Deployment: It can be quickly set up, making it ideal for areas with urgent connectivity needs.
- Flexibility: Easily scalable to accommodate growing subscriber demands.
- Accessibility: Bridges the digital divide by bringing connectivity to rural and underserved regions.
- Reliability: Less susceptible to damage from environmental factors compared to wired solutions.
Applications of WLL
Wireless Local Loop has diverse applications across various sectors:
- Residential Connectivity: Provides high-speed internet and telephony services to households, especially in rural areas.
- Enterprise Solutions: Enables businesses to establish reliable communication networks without extensive infrastructure.
- Emergency Services: Facilitates rapid deployment of communication systems during natural disasters or crises.
- Public Wi-Fi: Supports the creation of public hotspots in urban and remote areas.
Challenges of WLL
Despite its numerous advantages, WLL faces some challenges:
- Spectrum Availability: A limited frequency spectrum can constrain the deployment of WLL systems.
- Interference: Wireless signals are prone to interference from other electronic devices and environmental factors.
- Initial Investment: While cost-effective in the long run, the initial setup costs for base stations and equipment can be high.
- Regulatory Issues: Compliance with local telecommunication regulations can be complex and time-consuming.
The Future of Wireless Local Loop
As technology continues to advance, the potential of WLL is expanding. The integration of 5G technology promises to enhance WLL systems by offering faster speeds, lower latency, and improved reliability. Additionally, advancements in spectrum management and signal processing are expected to address current challenges, making WLL even more accessible and efficient.
Conclusion
Wireless Local Loop is revolutionizing the telecommunications landscape by providing an innovative alternative to traditional wired networks. Its cost-effectiveness, rapid deployment, and ability to bridge connectivity gaps make it a vital tool for achieving global digital inclusion. As technology evolves, WLL is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of communication.